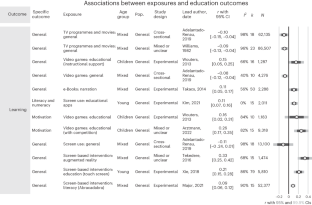
As screen time becomes more and more present in the lives of children, parents need the best information to help to guide their decisions. By collating all of the meta-analytic evidence from across the field, we hope to provide that evidence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
133,45 € per year
only 11,12 € per issue
Buy this article
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This is a summary of: Sanders, T. et al. An umbrella review of the benefits and risks associated with youths’ interactions with electronic screens. Nat. Hum. Behav. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01712-8 (2023)
Weighing the risks and benefits of screen time for children. Nat Hum Behav 8, 16–17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01713-7
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Get shareable link
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative